
What is a Web Crawler? How the Internet Gets Indexed
Web Crawler is a type of software application that is automated and is designed to browse the internet systematically. These bots “crawl billions of pages” every day before any ranking system even thinks about relevance. Their output, the index, now tops 100 petabytes of compressed data.
Yet most founders and marketers meet this army only when something goes wrong, e.g. a new landing page refuses to appear or Google’s status dashboard flashes a delayed indexing issue.
Break down:
Crawling: Bots fetch raw HTML, CSS and JavaScript via links, sitemaps or direct pings.
Rendering: Headless browsers execute scripts, so hidden text and SPA routes become visible.
Indexing: Parsed content enters massive, de-duplicated databases; canonical URLs win and clutter loses.
Serving: Ranking systems, passage indexing and now AI summaries pull from that index in milliseconds.
At each step, technical cues e.g, robots.txt rules, structured data, Core Web Vitals and even the lastmod date in your sitemap either help bots move faster or slow them down significantly. Manual fixes (URL Inspection, sitemap resubmits) still help, but push based automation like IndexPlease now fires pings the instant you hit Publish, ensuring crawlers get the right signals first.
1. Crawler 101: From Seed URLs to the Render Queue
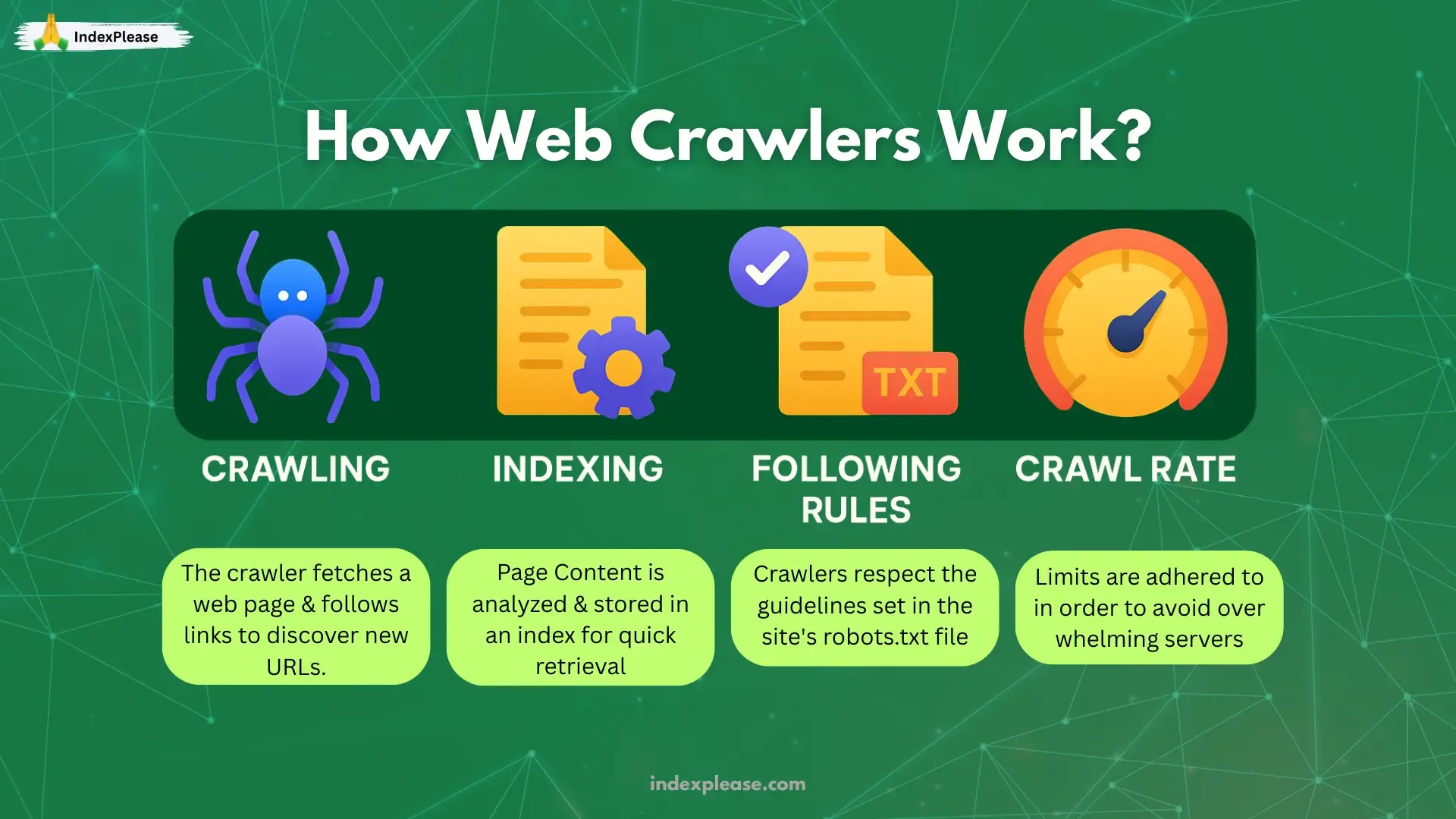
Imagine you’re asked to catalogue every book in the world, new titles arriving every second and you can only read a page or two before moving on. That’s a web crawler’s day job. Googlebot alone fetches billions of pages per day, according to Google engineering notes and it has to do so politely, efficiently and (in 2025) with a mobile-first lens.
1.1 Where Crawls Begin: Seed URLs
This process starts with a prioritized crawl queue made up of “seed” URLs pulled from:
Sitemaps you submit.
External links pointing to your site.
Push APIs like IndexNow or Google’s Indexing API (IndexPlease taps both).
Historical data Google constantly re-checks high value pages.
Each item enters a priority queue scored by its importance, change in frequency and host crawl-budget limits.
1.2 Fetch Pass (HTML Only)
Googlebot issues an HTTP request using its Smartphone agent.
Status code (200, 301, 404, etc.).
Raw HTML, no JavaScript yet.
Headers (Last-Modified, X-Robots-Tag).
1.3 Render Queue
After fetching, HTML is queued for rendering, where an automated browser processes JavaScript, CSS and generates the full DOM. Google’s JS-SEO basics page notes pages “may stay on this queue for a few seconds, but it can take longer” if resources are tight.
Why two passes? Speed. HTML is lightweight; JavaScript can be heavy. Splitting them lets Google crawl more URLs without melting servers.
1.4 Crawl Budget & Host Limits
Google caps hits per host to avoid overload, a concept called crawl budget. Large, slow sites slow down; fast, clean sites enjoy deeper crawls.
Quick wins to earn budget
| Lever | Effect |
|---|---|
| Core Web Vitals < 600 ms | Faster servers invite more requests. |
| Consistent 200s | Fewer 404/500s mean higher trust. |
| Accurate lastmod | Google skips unchanged pages, saving budget for new ones. |
| Indexing pings | Push only updated URLs |
IndexPlease automates the last two. It reads lastmod in your sitemap, then fires API pings so crawlers spend a budget on changed pages first.
Key Takeaway Crawlers are efficient but literal. They fetch what they can reach, render what isn’t blocked and delay hosts that slow them down. Give them clean HTML, open JS/CSS, clear robots rules and timely pings (IndexPlease makes that last part automatic) resulting in faster indexation.
2. Technical Signals That Help (or Block) Crawlers
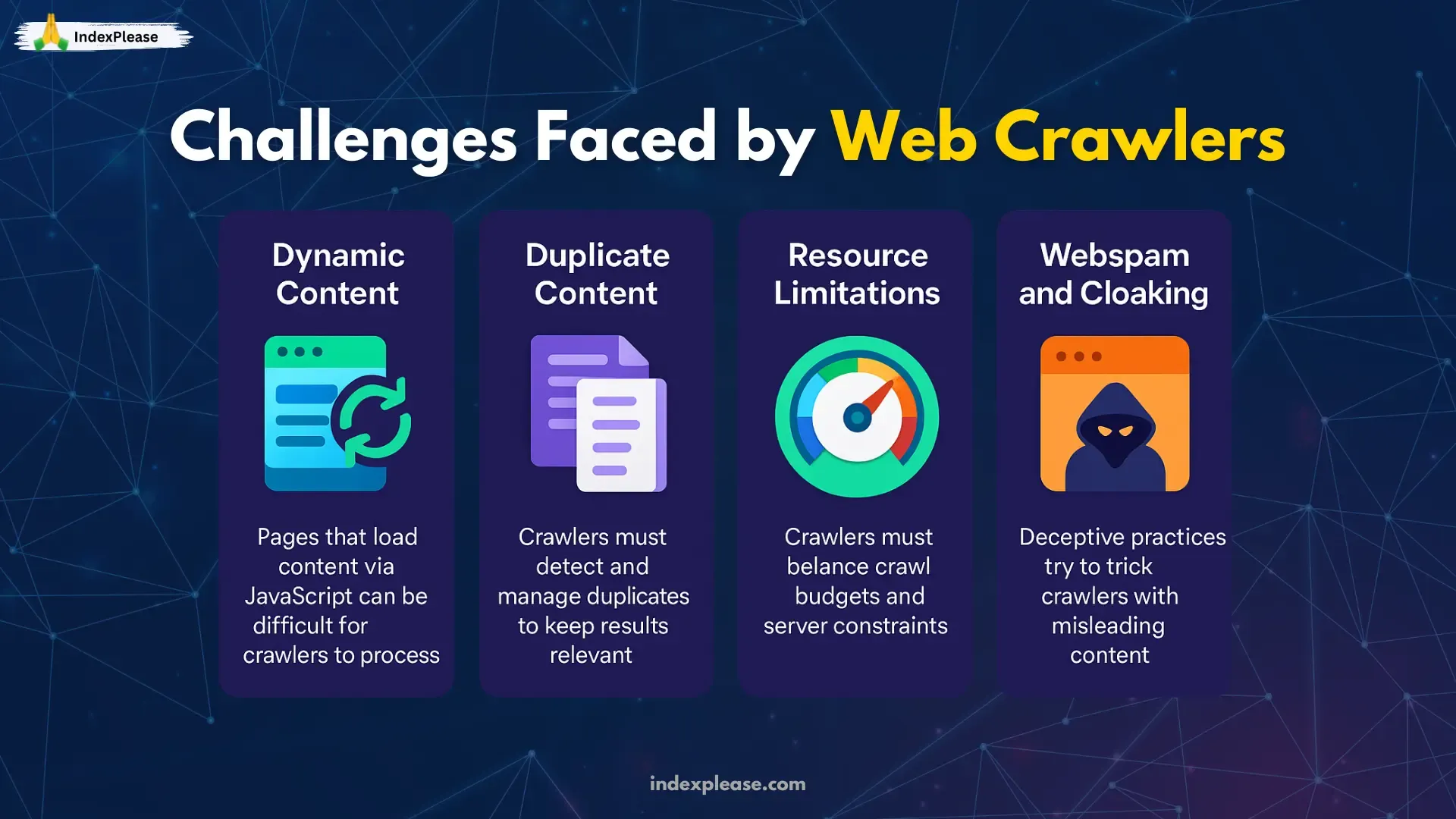
Crawlers are literal. They can’t “figure it out later.” They read the signals you give or don’t give and move on. Below are the key factors that accelerate or delay them. None require technical development work and most plug neatly into the automation flow that IndexPlease already watches.
2.1 XML Sitemaps
Google still calls the sitemap “the primary source of discovery for large sites.” Especially those with thousands of URLs or dynamic content that may not be easily reached through internal links alone. A well maintained sitemap ensures new pages are surfaced quickly, old ones are updated reliably and the entire site structure stays visible to crawlers, making it an essential foundation for scalable indexing.
2.2 Robots.txt
A single misplaced slash (Disallow: /products) can de-index a revenue category. Keep rules simple:
User-agent: * Disallow: /cgi-bin/ Disallow: /*?session= Sitemap: https://example.com/sitemap.xml
2.3 Structured Data = Faster Understanding
Moz’s 2024 study showed pages with valid Product or FAQPage schema were 33 % likelier to earn rich snippets and were crawled 12 % more often on news sites. This is the reason why following are essential for crawling:
Article / BlogPosting
Product (with price and availability)
FAQPage for support hubs
VideoObject for chaptered videos
2.4 Core Web Vitals
Google’s crawl team says servers that respond faster get crawled deeper. Semrush’s 2024 speed study backs it up; pages with green Core Web Vitals saw a 14% higher crawl frequency.
| Vital | “Good” Threshold | Quick Fix |
|---|---|---|
| TTFB | < 600 ms | Enable server level caching |
| INP | < 200 ms | Defer third-party scripts; self-host fonts. |
| LCP | < 2.5 s | Serve hero images in WebP/AVIF. |
2.5 Duplicate Defense
Google’s indexer consumes more resources when forced to differentiate between /Shoes and /shoes. Spell it out:
<link rel=“canonical” href=“https://example.com/shoes”\>
Redirect non-preferred hosts (no-www → www).
Force lowercase slugs in your CMS.
Update internal links so the canonical is always the one you link to.
IndexPlease only pings canonical URLs, you won’t waste crawl budget on rogue variants.
3. FAQs
How Often Do Web Crawlers Visit Websites?
This is really different for each site. For example, Google’s crawl rate can be just a few visits every day for popular sites, to more limited activity for those still coming under the radar. This process can be accelerated by using IndexPlease’s search indexing tool.
Can I Block Web Crawlers from My Website?
Yes. Using tools such as robots.txt files and meta tags can block web crawlers from specific pages to reduce indexing.
Do Web Crawlers Follow Links in JavaScript Code?
Modern web crawlers can sometimes follow JavaScript links, but HTML links are more consistently indexed.
How Can I Check if My Website Has Been Indexed by Search Engines?
To check index status, you might want to use IndexPlease’s search index tool, or Google and type site:yourdomain.com.
Are Web Crawlers Capable of Reading Images and Videos?
Web crawlers read image and video metadata but interpret text more comprehensively than visual media.
Can Web Crawlers Access Password-Protected Content?
No. Web crawlers usually have no access to password protected content because that is restricted to people who are already authorized.
Final Thoughts
Web crawlers are the internet’s librarians. Give them a clear path, clean HTML, open resources, a fresh sitemap, structured data, timely pings and they’ll shelve your content where buyers can find it. Starve them of signals, block essential JS or drown them in duplicate URLs and they’ll pass you by.
The modern formula is push-first:
Accurate Sitemap
Canonical URLs only
Structured data so the indexer “gets” your entities.
Automated pings so crawlers learn about changes now, not next week.
That last step is where IndexPlease earns its keep. One webhook or sitemap import and:
Detects new or updated URLs instantly.
Sends them via Google’s Indexing API (where eligible) and IndexNow for Bing, Yandex, Naver and Seznam.
Skips unchanged pages, preserving quotas and crawl budget.
Next move: Spin up a free IndexPlease trial, publish your next article and check Search Console tomorrow, you’ll see Indexed (Smartphone). Less waiting, more ranking and that’s how modern SEO should feel.