
What Is a URL and How Does It Impact Indexing?
Open any browser tab and the first thing you meet is a URL which is the string that tells crawlers where your content lives and indirectly, whether it deserves to rank. Every page level signals links, freshness and Core Web Vitals gets glued to that exact address. Change the structure or create duplicates and you risk compromising your authority.
Marketers know the pain. Semrush’s 2024 Site Audit dataset flagged “duplicate content caused by URL parameters” as a top-five crawling error across 180 million pages, often delaying indexation for weeks. Meanwhile, Google’s own URL-structure guidelines warn that inconsistent capitalization, stray trailing slashes, or needless UTM strings can force the crawler to “spend extra resources figuring out whether two addresses are actually the same page.”
Why does it matter more in 2025?
Crawl-Budget Economics: Googlebot Smartphone now handles 100 % of discovery; wasted URLs eat the budget that should fetch fresh content.
AI Overviews & Entity Mapping: Google’s AI answers pull canonical URLs directly; if you split equity across ?sort= and ?color= variants, you may disappear from the summary box altogether.
Instant-Ping Culture: Tools like IndexPlease can notify multiple engines the moment a canonical URL changes.
In other words, your URL isn’t just an address; it’s a passport carrying every ranking stamp your page earns. Get it right and indexing is swift and click-through rates rise (short, keyword-rich slugs lifted CTR by 8 % in Semrush’s 2024 slug study. Get it wrong and you’ll spend months resolving indexing issues.
1. URLs 101
When you glance at a link like https://store.example.com/products/blue-running-shoes?sort=price#reviews. Every word you write sends a signal to Google. When everything’s clear and in the right place, crawlers move through the site easily. When things are messy, you slow down crawling, confuse what should be indexed and lose the user’s trust.
Here’s a simple breakdown of why each piece matters:
| Part | Example | Why Crawlers Care |
|---|---|---|
| Protocol | https:// | Google confirmed in 2014 that HTTPS can be a lightweight ranking factor and in 2025 almost every site defaults to it. |
| Subdomain | store. | Google treats subdomains as separate entities for crawl budget. Use them only when content truly differs (e.g., blog vs app). |
| Domain | example.com | Your brand’s root authority. Stick to one preferred version (https://www. or not) to avoid duplicate indexing. |
| Path | /products/ | Indicates topical hierarchy. Google’s URL best-practice doc suggests keeping paths logical but shallow for faster discovery. |
| Slug | blue-running-shoes | A clear, hyphenated slug helps users and crawlers guess relevance, |
| Parameters | ?sort=price | Useful for filters, dangerous for duplicate bloat. Google may crawl endless combos unless you set clear limits. |
| Fragment | #reviews | Ignored by Googlebot for indexing; fine for jump links but never hide unique content behind it. |
1.1 One URL = One Piece of Content
Google treats each unique string up to the fragment (#) as a separate address. Change capitalization, add a trailing slash or tack on ?ref=twitter and you’ve potentially created a new crawl target.
Quick Necessary Checks
Pick one casing, lowercase is simplest.
Redirect non-www to www (or vice-versa) site-wide.
Decide if /page or /page/ is canonical; 301 the other.
Time-saver: Once your canonical pattern is set, drop those URLs into IndexPlease. Each time you publish, it pings Google, Bing and Yandex with the preferred address, keeping duplicates out of the crawl queue.
1.2 Parameters: Friend, Foe, or Both?
Parameters start after “?” and stack with “&”. Useful for filters (?color=blue) but deadly when multiplied. Google’s ecommerce URL guide lists runaway parameters as a top cause of slow indexing.
Best practice
Show the clean version in internal links (/products/blue-running-shoes).
Add a canonical tag from every parameter version → clean URL.
Block truly useless combos (?sort=oldest&view=all&session=123) via robots.txt or the URL Parameter Tool (still available in Search Console).
1.3 Why Slugs Deserve Craftsmanship
Use words, not IDs, descriptive words & hyphens between words. Semrush’s test across 10k e-commerce pages found human readable slugs improved click through by nearly a point versus numeric IDs.
Slug quick-start
Keep it under 60 characters.
Use lowercase, hyphens and avoid stop words like “and,” “the.”
Match the main keyword once; stuffing multiples doesn’t help.
1.4 Clean vs Messy
| Clean, Crawl-Friendly URL | Messy, Duplicate-Prone URL |
|---|---|
| https://shop.example.com/shoes/blue-running-shoes | http://example.com/prod?id=12345&utm_source=email&sort=asc |
| One canonical address → faster indexing. | Multiple variants → wasted crawl budget, split signals. |
Takeaway
A URL isn’t just a pointer; it’s the first ranking signal your page ever sends. Keep the structure simple, case-consistent, parameter-lite and descriptive. Then let IndexPlease broadcast that single, canonical version across every search engine the moment it goes live so crawl budget is spent where it counts.
2. Canonicalization & Duplication
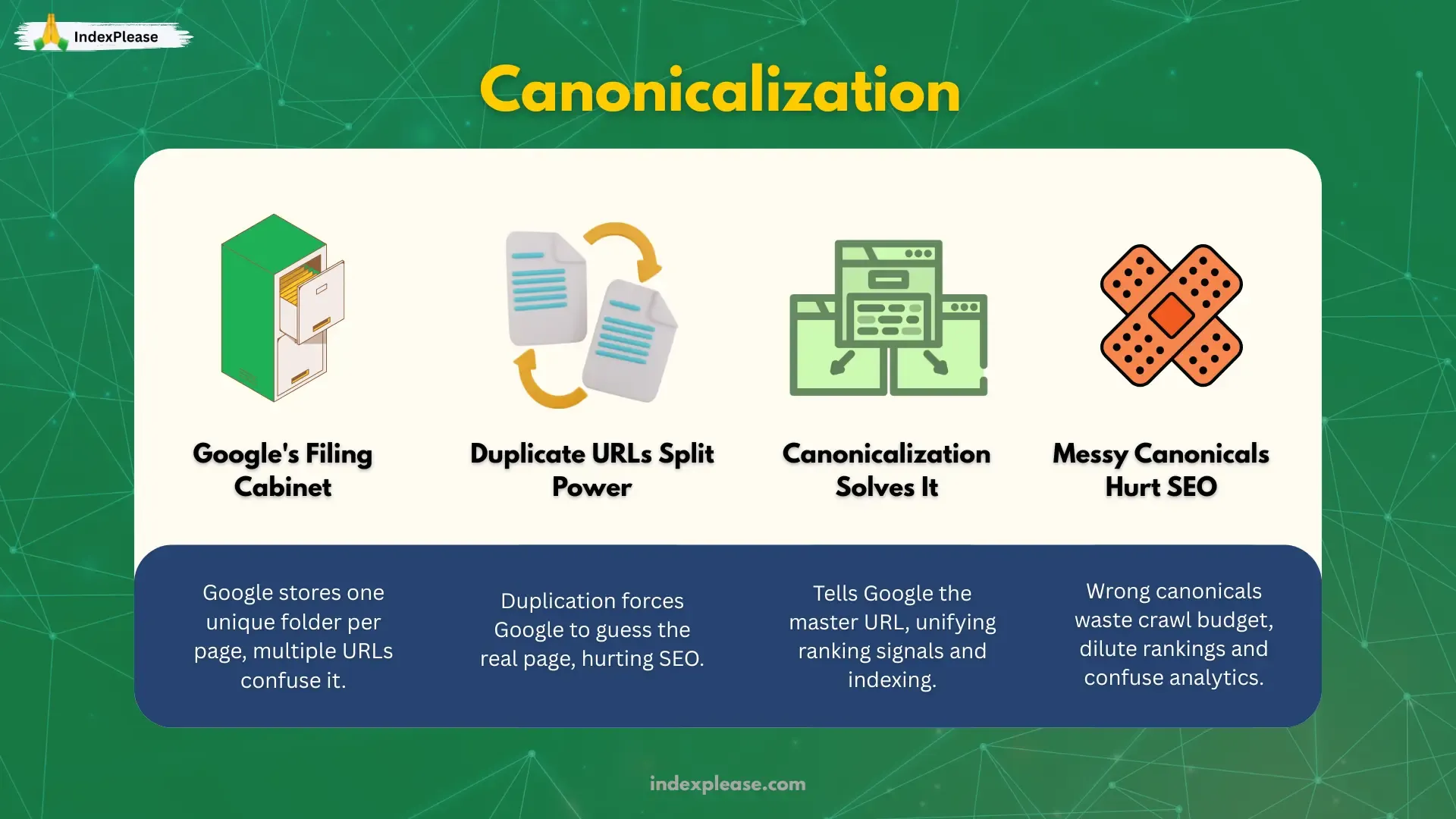
Picture Google’s index as a massive filing cabinet. Every page you publish gets its own folder, but if you let multiple URLs reach the same content, Google has to guess which one is “the real file.” That guessing process is called canonicalization and when Google picks the wrong version or can’t decide, ranking signals split, crawl budget bloats and analytics get disturbed.
2.1 Why One Page Can Wear Ten Costumes
Duplicate URLs show up in sneaky ways:
www vs non-www – www.example.com/shoes vs example.com/shoes
Trailing slash – /shoes vs /shoes/
Case differences – /Blue-Shoes vs /blue-shoes
Parameters – /shoes?ref=twitter, /shoes?sort=price
HTTP vs HTTPS
2.2 How Google Picks a Canonical
Google weighs several clues:
Rel=canonical tag: An HTML hint pointing to the preferred URL.
HTTPS & Sitemap entries: Secure and map listed URLs win.
Internal links: The version your own site links to most often.
Redirects: 301s consolidate signals.
Content match: Near identical copies trigger a decision.
If you don’t guide Google, it’ll make choices for you and you might not like them. Messy backlinks with random parameters or uppercase URLs can make things difficult.
2.3 Five Easy Canonical Rules
| Rule | What to Do | Why |
|---|---|---|
| Pick one protocol | Redirect HTTP → HTTPS site-wide. | Mixed versions split link equity. |
| Pick one host | Redirect non-www → www or vice-versa. | Consolidates domain signals. |
| Pick one slash style | Either /page or /page/, then 301 the other. | Avoids duplicate crawls. |
| Use lowercase in slugs | /blue-running-shoes not /Blue-Running-Shoes. | Case is a unique URL to Google. |
| Tag the canonical | <link rel="canonical" href="https://example.com/shoes" > | Gives Google an explicit hint; Ahrefs calls it the “seatbelt of SEO.” |
Shortcut: once you set that clean canonical, drop it into IndexPlease. The platform pings Google, Bing, Yandex and Naver the moment the page goes live, so crawlers learn your preferred URL first before messy links start spreading.
2.4 Dynamic Parameters vs Crawl Budget
Sorting, filtering and campaign tags can explode a single product into dozens of URLs. Googlebot may crawl them all, spending a budget that should fetch new content.
2.5 Multi Locale Sites (Folders vs Subdomains)
If you serve content in example.com/fr/ and fr.example.com, Google will treat them as separate sites, which splits your authority. Unless there’s a really good server reason, stick with subfolders and use hreflang. It keeps your domain’s trust strong and avoids messy canonical issues.
Key Takeaways
Every unique string (before #) can become a standalone page in Google’s eyes.
Clean canonical tags, proper redirects and lowercase URLs help keep all your SEO power tied to one link.
When parameters get scattered, they drain your crawl budget fast.
IndexPlease makes sure the right version of your page is the first thing search engines see.
3. Dynamic Parameters & Crawl Budget
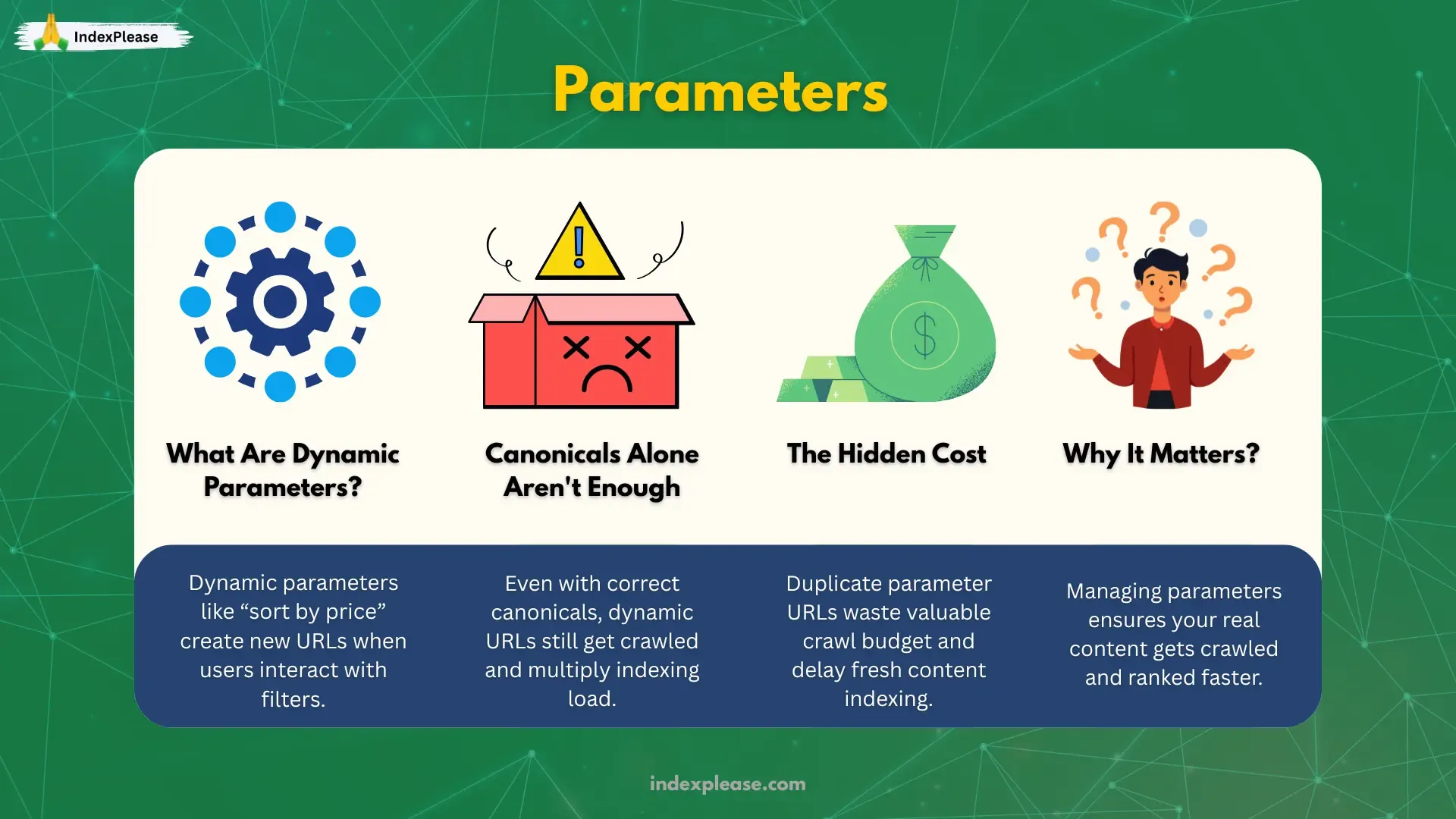
Even with a correct canonical URL, actions like “Sort by price” can add parameters, creating new URLs for Google to crawl. At scale, this leads to near duplicate pages that waste crawl budgets, diverting resources away from indexing your content.
3.1 Why Parameters Multiply So Fast
Filters & Facets: /shoes?color=blue&size=9
Sort Orders: ?sort=price or ?order=asc
Tracking Tags: ?utm_source=newsletter
Session IDs: ?session=12345
Unmanaged parameters waste crawler hits on up to 30% of large-site URLs, sometimes leaving important pages not crawled for days.
3.2 How Google Handles Parameters Today
Crawls a sample to see if content changes.
Groups obvious duplicates into one cluster.
Chooses a canonical, often the clean and parameter-free version.
3.3 Crawl-Budget Math
Googlebot allocates a crawl quota per host based on server speed, link equity and freshness. Every unnecessary parameter URL costs a hit that could have gone to new or updated content.
3.4 Tools & Settings
| Tool | What It Does | Warning |
|---|---|---|
| Search Console – Settings → Crawl Stats | Shows hit count by response & purpose. | No parameter break-out, requires log analysis. |
| URL Parameter Tool | Tell Google how to treat specific parameters. | Google plans to phase it out; use canonical tags long-term. |
| Semrush Site Audit – Crawl Budget Waste | Flags URLs with unnecessary parameters. | Snapshot only; combine with server logs for full picture. |
| Log-file Analyzer (Screaming Frog/Ahrefs) | Reveals exactly which param URLs Googlebot crawls. | Needs server log access. |
3.5 Handling URL Parameters
Serve clean internal links: Keep ?sort= out of navigation.
Canonicalize useful parameters: for example /products?color=blue if “blue shoes” has search demand.
Block or strip the rest: Session IDs, tracking tags and print views.
Ping fast: Once changes are live, IndexPlease can notify engines so clean URLs enter the index first, saving budget automatically.
4. FAQs
1. Should I stuff keywords into every URL slug for better rankings?
No. One clear phrase that describes the page is perfect (e.g., /blue-running-shoes). Simple Rule: 3–6 words, lowercase, hyphens and no stop-words.
2. When do I use a 301 redirect versus a rel=canonical tag?
Use 301 when the old URL should disappear forever. Use Canonical when duplicates must stay live but you want Google to credit one master page.
3. Can I drop the .html or .php at the end of my URLs?
File extensions have no impact on rankings. As long as the redirects are clean, Google treats both formats the same.
4. Do capital letters in a URL really matter?
So, basically /About and /about are different files. Google will crawl both if they exist, splitting equity. Pick lowercase URLs consistently.
5. How short is too short for a slug?
Google doesn’t penalize conciseness, but one-word slugs like /p7x8 lack context and hurt click-through. Aim for 10–60 characters. Moz’s 2024 best-practice note: “If a human can’t guess what’s behind the link, revise.”
Final Thoughts
URLs may look dry, but they’re the first element Google stores, the only label users see in a SERP (Search Engine Results Page) preview and the glue that holds every ranking signal you earn. Keep them short, lower case, descriptive, parameter lite and consistently canonicalized. Then safeguard your crawl budget:
Canonicalize or redirect duplicates.
Guide parameters with tags, tools or robots.txt
Tell engines fast, that’s where IndexPlease shines.
The moment your clean URL goes live, IndexPlease pings the Search Engines making sure your canonical version is what they crawl first. Less duplicate clutter, more ranking power.
Next move: Start a free IndexPlease trial, add your sitemap and watch clean URLs appear in Google’s “Indexed” report within hours, not days. Your content team can focus on pages that convert while the indexing stays flawless.