Looks like IndexPlease from @amosbastian is working wonders for the Google index of @WhatPulse 💪
Fast Website Indexer
An Ultimate
URL Indexing Tool
Our advanced website indexer ensures quick URL indexing, boosting your website's visibility.
Get your SEO efforts rewarded on google with our rapid indexing tool.
How to index with IndexPlease?
IndexPlease Links Indexing Service is quite straightforward to setup—just follow these simple steps.
Sign up for Free
Go to IndexPlease Dashboard, and easily sign up for free with an email or Google Account.
Create a workspace
Create a workspace with a unique name (when you sign in for the first time). In IndexPlease, a workspace is place where you attach your subscription, your sites, sitemaps & URLs. You can create more than one workspaces.
Add your websites
Import Sites from your Google Account to work with, add our Service Account to your sites in GSC and Bing key at your site’s root. Finally, enable Auto Indexing to boost your SEO indexing.
Sit and relax
Subscribe to a suitable plan. And you’re done. IndexPlease will keep reviewing your website URLs and submit them to index on Google, Bing, that are not indexed. No manual effort required—our auto indexing tool will handle everything.
Get indexed on Google,
Drive traffic
It is an important step in SEO to get indexed on Google to drive more traffic and to boost your online presence effortlessly. You won’t get any organic impressions or clicks until Google knows your website and has indexed it’s pages.
Get StartedInstant Indexing,
Manually index any page
Immediately re-submit an updated page to index on Google or manually index any page on your site. Our Instant Indexing Tool allows to bulk index hundreds of pages in one click. You can do it right from the Dashboard of IndexPlease for free. You can shift your focus on creating content and we will help you getting it indexed immediately.
Get StartedBulk indexing,
with one click
Either you can manually submit your pages to get indexed one at a time in Google Search Console or let the IndexPlease handle the indexing for you. And you can use your time better working on marketing. It’s your choice.
Get StartedTurn on,
auto indexing
After you turn on ‘auto indexing’ on your website with IndexPlease, you can leave your Google indexing status with us. IndexPlease will daily scan your site for new and unindexed links and automatically index them. We’ll also email you the daily indexing progress on your sites.
Get StartedIndexing history,
Watch being indexed
See your site’s indexing progress over time on our Dashboard to get an understanding of each indexing job that how Google recognizes your site.
Get StartedWhat people are saying
Loads of businesses are using IndexPlease to grow their organic traffic
Have been using indexplease.com by @amosbastian alongside some SEO improvements. In the past month compared to 3 months, I have gone from: - 60% indexed to 100% - Click through 3.1 > 3.9% - Page views (monthly) 3.2k > 3.8k And that for only one site Validated? YES
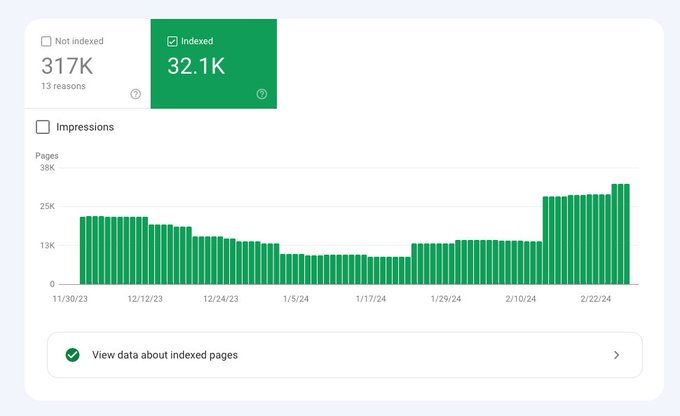
If this is not a successful case study for @amosbastian's indexplease.com, then I don't know what is. Before: ~2k / ~30k indexed Now: ~20k / ~30k indexed Thanks @amosbastian for making this awesome tool! 🙏
Looks like IndexPlease from @amosbastian is working wonders for the Google index of @WhatPulse 💪
Have been using indexplease.com by @amosbastian alongside some SEO improvements. In the past month compared to 3 months, I have gone from: - 60% indexed to 100% - Click through 3.1 > 3.9% - Page views (monthly) 3.2k > 3.8k And that for only one site Validated? YES
If this is not a successful case study for @amosbastian's indexplease.com, then I don't know what is. Before: ~2k / ~30k indexed Now: ~20k / ~30k indexed Thanks @amosbastian for making this awesome tool! 🙏
Looks like IndexPlease from @amosbastian is working wonders for the Google index of @WhatPulse 💪
Have been using indexplease.com by @amosbastian alongside some SEO improvements. In the past month compared to 3 months, I have gone from: - 60% indexed to 100% - Click through 3.1 > 3.9% - Page views (monthly) 3.2k > 3.8k And that for only one site Validated? YES
If this is not a successful case study for @amosbastian's indexplease.com, then I don't know what is. Before: ~2k / ~30k indexed Now: ~20k / ~30k indexed Thanks @amosbastian for making this awesome tool! 🙏
Pricing Plans for Teams of All Sizes
Saves upto 50%
Starter
For people starting their SEO journey
$15$7/month, billed annually
- Index 400 pages/day
- Auto-index 3 sites
- Unlimited URLs
- Unlimited GSC Accounts
- SEO Meta Tags Previews
- Open Graph Previews
- Page Errors Monitoring
Growth
The essentials to get all your pages indexed
$35$17/month, billed annually
- Index 1000 pages/day
- Auto-index 10 sites
- Unlimited URLs
- Unlimited GSC Accounts
- Page Errors Monitoring
- SEO Meta Tags Previews
- Open Graph Previews
Professional
A plan that scales with rapidly growing businesses
$65$33/month, billed annually
- Index 2000 pages/day
- Auto-index 20 sites
- Unlimited URLs
- Unlimited GSC Accounts
- Page Errors Monitoring
- SEO Meta Tags Previews
- Open Graph Previews
Enterprise
For agencies and large businesses with large sites
$65+$33+/month, billed annually
- Index 2000+ pages/day
- Auto-index 20+ sites
- Unlimited URLs
- Unlimited GSC Accounts
- Page Errors Monitoring
- SEO Meta Tags Previews
- Open Graph Previews