
Search Engine Indexing Process: How It Works and Why It Matters
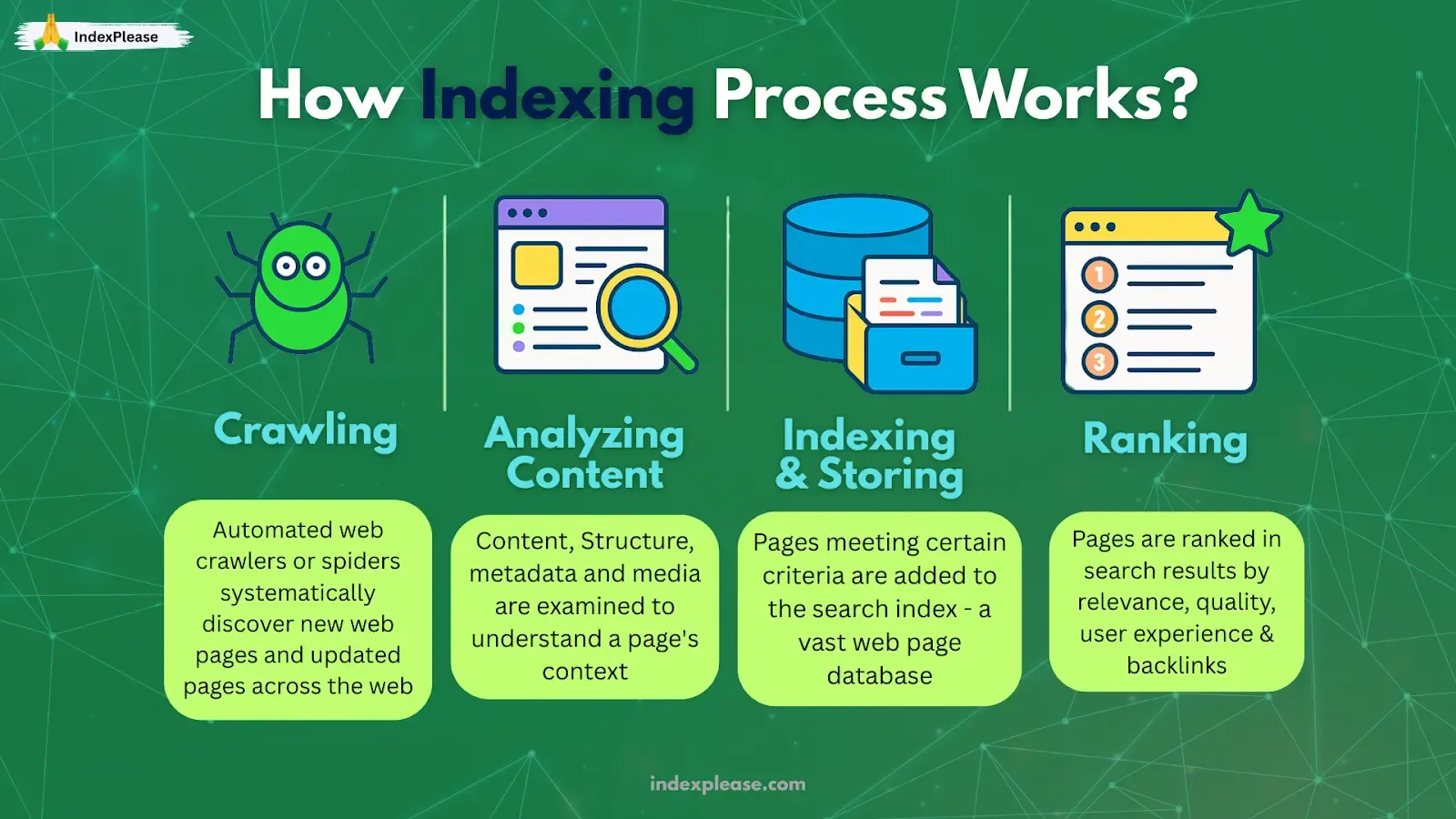
Search engine indexing is the process by which search engines organize and store information collected from web pages during crawling. Search engines can’t index what they can’t reach. The first hurdle in the journey from “publish” to “rank” is a two-step handshake: crawling (grabbing raw files) and rendering (executing JavaScript/CSS) so the page looks the way users see it.
1. Meet Googlebot Smartphone, the Only Crawler That Matters
Since July 5 2024, Google fetches every site with its smartphone agent and retires desktop crawling except for rare comparisons. If a page isn’t accessible or is half-empty on mobile, it’s effectively invisible.
Practical takeaway
Test your URL in Search Console’s URL Inspection → you’ll see a “Crawled as: Googlebot Smartphone” stamp.
Any content hidden on mobile (expanders, lazy JS) won’t reach the index.
1.1 How Crawling Actually Happens
Discovery: Google finds a link in your sitemap, on another site or via an API ping.
Fetch: Googlebot requests the raw HTML, recording server headers, status codes and canonical hints.
Queue: The HTML is queued for rendering, Google calls this the Render Queue.
Render: JavaScript runs additional resources load. Google’s December 2024 crawling explainer says this step can be delayed “by minutes to days” depending on site health and crawl budget.
Why split fetch and render? Efficiency. Google can fetch millions of pages quickly, then batch-render them when resources free up.
1.2 Where Things Go Wrong
| Issue | What Googlebot Sees | Result |
|---|---|---|
| Blocked resources (CSS/JS in robots.txt) | Blank layout | “Submitted URL blocked by robots.txt” |
| Heavy client-side JS | Empty <body> in HTML pass | “Indexed, though blocked by robots.txt” or missing content |
| Slow Core Web Vitals | Timeouts during fetch | Crawling frequency drops; render delayed |
Semrush’s 2024 site speed report shows pages scoring red on Core Web Vitals get crawled 14% less often than green ones.
1.3 Linking Discovery to Rendering and Why It Matters for Modern SERPs
Google’s AI Overviews and “Perspectives” carousels pull live-rendered snippets, not raw HTML. If your FAQ content only appears after a JS click, it might never be indexed. Ahrefs’ “How Google Indexes” guide (Feb 2025) notes sites that switch to server side rendering often regain lost FAQ rich results within two re-crawls.
Master crawling and rendering can clear the gate to the next stage: indexing, where Google decides if, where and under which canonical URL your content belongs.
2. How Search Engines Store, Deduplicate and Rank Your Pages

After Googlebot crawls and renders a page, the raw HTML, the rendered DOM (Document Object Model) and all outbound links are stored in a massive database known as the index. Think of it as a library card catalog: each URL gets its own card, stamped with keywords, link data and freshness dates. If the crawl stage was about finding pages, indexing is about filing them where Google can reach for an answer in milliseconds.
2.1 What Happens Inside the “Indexer”
Parsing: Google removes standard page elements and extracts headings, anchor text, structured data (JSON-LD), and image alt attributes.
Canonical Check: It compares duplicate URLs and picks a master version (the canonical).
Link Graph Merge: Internal & external links pointing at the canonical consolidate into one authority score.
Miss any canonical tag and Google may choose the wrong URL.
2.3 Entity Extraction & Structured Data
Google’s index isn’t just keyword tokens; it stores entities, people, products and prices. Structured-data (Schema.org) feeds that entity layer. Moz’s December 2024 study showed pages with valid Product or FAQPage schema were 33% more likely to earn rich results.
Must have content in 2025:
ArticleorBlogPostingfor authoritative contentProduct(withprice,availability) for e-commerceFAQPagefor quick-answer eligibilitySpeakablefor voice devices
24. Passage Indexing & AI Overviews
From 2023, Google can rank a single paragraph (passage) from a long article. Proper headings (<h2>, <h3>) and clean DOM order help the indexer isolate those passages. That same passage data now feeds AI Overviews. If your FAQ lives behind a script that renders late, the indexer may never store it so the AI answer box quotes your competitor instead.
Takeaway
Indexing is where crawler discoveries become searchable assets. Reliable canonical tags, concise URLs, structured-data and up-to-date lastmod fields give Google enough confidence to file the page quickly often within hours when paired with instant pings from tools like IndexPlease.
3. Serving: From Index Shelves to SERP
Your page is crawled, rendered and neatly filed in Google’s index. Great, except nothing happens until a user types a query. That final hop from stored document to search result is called serving and in 2025 it’s a far tougher arena than “ten blue links.”
3.1 Ranking Has Turned Into Retrieval + AI Selection
Traditional ranking still scores pages on relevance, freshness, authority and UX. But Google’s serving layer now does extra work:
Passage retrieval: Google can surface a single paragraph from your 2000 word guide for a long-tail query. It only works if the passage was rendered and indexed correctly.
Result diversification: Images, videos, Products, Perspectives and Discussion cards all fight for limited space.
AI Overviews: A generative summary that often sits above every organic listing.
When an AI Overview is present, traditional organic links lose noticeable traffic, especially on informational searches.
Semrush’s December 2024 Sensor snapshot shows AI Overviews appear on 14 % of mobile queries and climbing. The obvious takeaway: if your URL isn’t selected as a citation inside that box, you could miss the click entirely.
3.2 How Clean Indexing Boosts Your “Serve” Odds
All of the fancy outputs above draw from the same verified, canonical copy in the index. If Google is unsure which URL is canonical or your key content never rendered, you get filtered out before ranking even begins.
Passage indexing uses the rendered DOM. Missing headings or lazy-loaded text? That paragraph can’t rank.
AI Overviews choose citations from “high-quality, canonical pages.” Duplicate chaos or parameter junk lowers your trustworthiness.
Rich results (FAQ, HowTo, Product) only display if Google can parse valid Schema and that lives in the canonical.
3.3 Speed Matters Here, Too
Google often boosts newer or recently updated content, especially for topics where timing matters (like news, trends, events, updates). Automated pings through platforms like IndexPlease help close that gap, moving discovery from hours to minutes and giving fresh content a better chance to surface while it’s still trending.
3.4 Serving Best Practices
Front-load Key Info: Google trims snippets; the first 100-120 characters of a paragraph influence AI Overviews and passage ranking.
Use Descriptive Headings:
<h2>How long does it take to index?helps Google match a passage answer and cite you.Match Schema to Visible Text: Google drops FAQ rich results when schema answers don’t appear on the page.
Keep Canonicals Clean: The serving system respects the index’s “master” URL. If your canonical flips due to clutter, you lose accumulated ranking signals.
Ping Quickly: Tools like IndexPlease push fresh canonicals putting updated content back on SERP shelves within hours.
You can’t control every AI box, but you can make sure Google sees the cleanest, freshest and fully rendered version of your page. It begins with strong crawling and indexing foundations and ends with rapid update signaling, the exact automation IndexPlease was designed for.
FAQs
How can I improve my chances of getting better registered index notifications by the search engines?
To enhance indexing, make sure to enable access for crawlers by making an XML sitemap and submitting it through IndexPlease. Make sure your content includes pertinent keywords, creates a structure with descriptive title and headers and includes proper internal linking. Regularly updated, high-quality content also encourages thorough indexing.
Will I Need to Encourage Search Engines to Crawl My Site?
No, search engines will inevitably discover your website and crawl it. Nevertheless, this can be expedited by submitting your sitemap with webmaster tools like IndexPlease.
Will I Need to Notify Search Engines When Adding New Content?
Not necessarily, but notifying search engines can speed up indexing for new content. This can be done by requesting an index through Google Search Console URL Inspection Tool or by submitting an updated sitemap.
Will Search Engines such as Google Ever Remove Content?
Yes, search engines have the ability to remove content due to lack of accessibility, violation of guidelines or bad signals. Google Search Console allows you to track your content’s indexing status and take actions to resolve deletion issues.
What is the Process to Get Deleted Content Back into The Index?
Remove all the issues that are causing content to be taken off and then request for re-indexing through IndexPlease’s indexing tool or resubmit the page’s URL in the sitemap.
Final Thoughts
The indexing pipeline is the beating heart of search visibility. Crawl, render, file and serve. When any stage slows, your content stalls when each stage is optimized, you unlock rich snippets, AI citations and faster revenue cycles.
Here’s the modern formula:
Render-ready pages: Mobile HTML, CSS/JS unblocked, sub-600 ms Core Web VItals.
Canonical clarity: One clean URL, consistent internal links,
<link rel="canonical">.Structured data: So the indexer understands entities and freshness.
Proactive pings: So crawlers hear about changes quickly.
Manual methods still have a place for first-run Quality Assurance or emergency patches whereas Automation flips the script: clean signals in, duplication out, pages indexed within hours.
That’s exactly what IndexPlease was built for. Point it at your sitemap, and it:
Detects new or updated URLs
Pings Google’s Indexing API where eligible and IndexNow for Bing, Yandex, Naver and Seznam instantly.
Logs responses so you see how fast every page is crawled and filed.
Next step: start a free IndexPlease trial, publish your next article and see “Indexed (Smartphone)” appear in the Search Console within minutes. Faster indexing and accelerated visibility are essential to how modern SEO should operate.