Search engines are the treasures of the information that powers the digital world. Well this information is gathered from the websites? You might be wondering, how search engines and websites interact? Robots.txt is responsible to perform this task. It is a tiny yet effective file that controls how search engines interact with your website. In short, robots.txt is a guide for the crawlers that specifies which areas of your website are for them to visit.
Understanding how robots.txt influences indexing can help your website index and rank. This article discusses important details of robots.text and its role in website indexation.
What is Robots.txt?
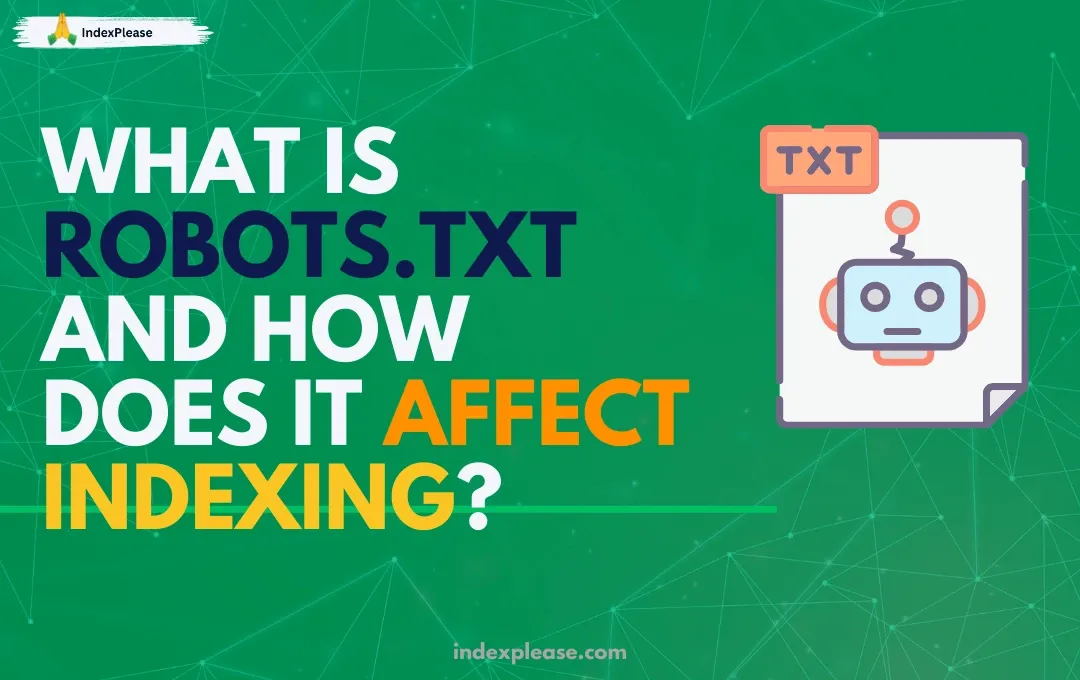
Robots.txt is a text file stored in a website’s root directory. Its main goal is to control crawler activity so bots don’t view useless or sensitive pages. Let’s say you are planning a party. Even though you want everyone to enjoy the main hall, you would prefer they stay away from your storage room or private office. Likewise, you can specify which parts of your website are “open to users” and which are not by using the robots.txt file.
For example, you can tell bots not to index sections of your website that are not optimized, have duplicate content, or have login pages. Although it seems little, this affects how well your website performs in search results. However, it’s crucial to remember that robots.txt is more of a recommendation than a rigid guideline and some bots may still be able to access restricted places.
How Does Robots.txt Affect Indexing?
Search engines such as Google and Bing use bots to crawl websites and collect data to index and rank them. The number of indexed pages on the website directly depends on how you set up your robots.txt file. Unintentionally blocking important pages will prevent them from appearing in search results. On the other hand, you can increase a website’s ranking by directing bots to crawl only relevant content.

E-commerce websites, for instance, often use robots.txt to block pages with outdated products or confidential client information. This targeted crawling ensures that search engines give priority to valuable content. On the other hand, incorrect use of robots.txt may lead to decreased visibility and wasted opportunities for natural traffic. So, an organized strategy is crucial when choosing what to allow or prohibit.
Setting Up a Robots.txt File for Effective Indexing
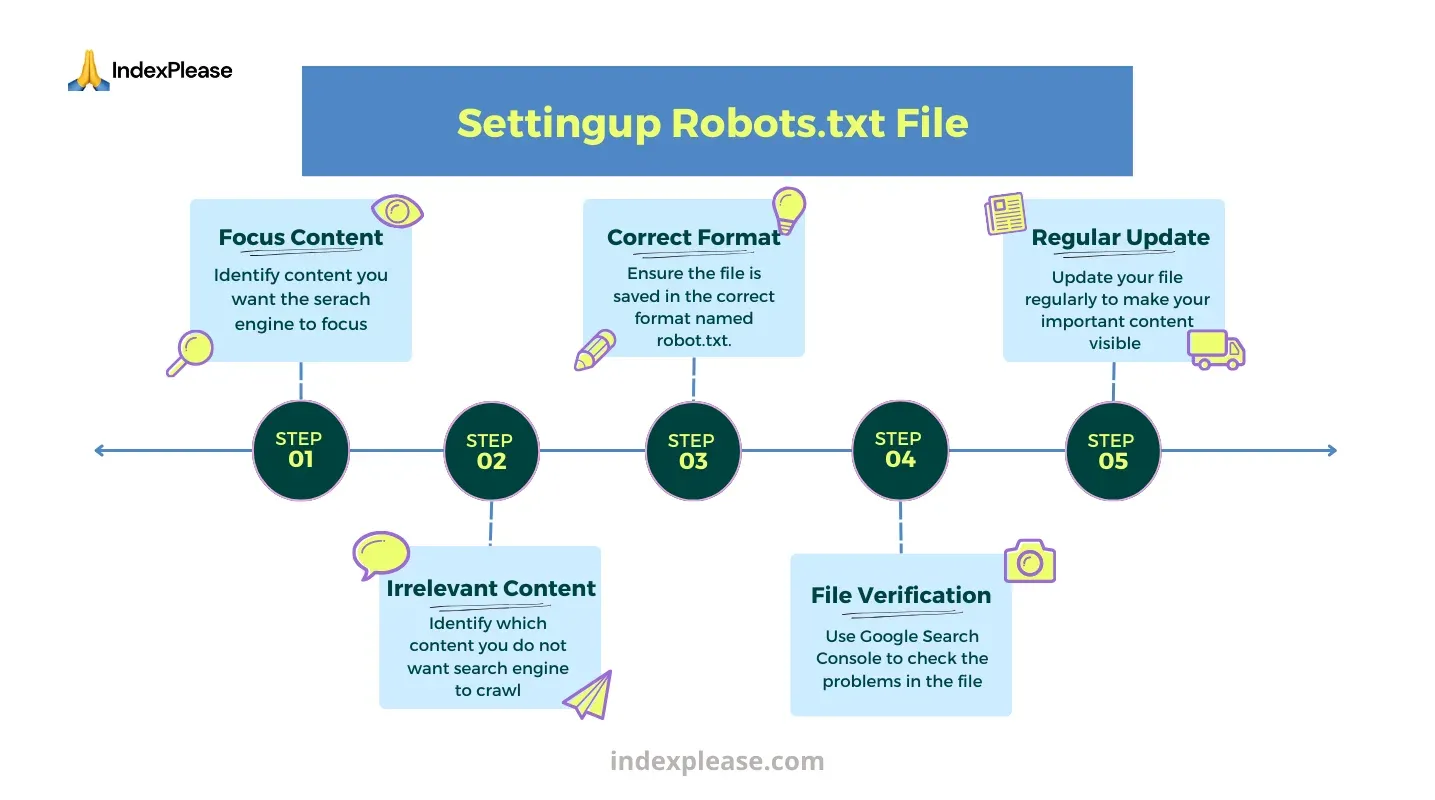
Creating a robots.txt file is a simple procedure that can significantly enhance the indexing of your website. Search engine bots can use this file as a guide to learn which sections of your website to crawl and which to ignore. To get started, determine what content you want search engines to focus on. Generally, we do not include
Private spaces
Duplicate pages
Sections that are still not ready
Once you have determined the content areas, create brief and clear guidelines defining what bots can and cannot access. Ensure the file is saved in your website’s root directory and named “robots.txt.” Using programs like Google Search Console to check the file for problems is essential. If you regularly check and update the file, search engines can effectively index the most valuable content while ignoring irrelevant fields.
Best Practices for Using Robots.txt with Search Engines

Effective use of robots.txt requires a combination of accuracy and strategy. The following are some suggested practices:
i) Keep It Simple
A simple robots.txt file reduces errors and confusion and removes extremely complicated rules that could confuse search engine bots. Use specific directives to indicate exactly what should or shouldn’t be crawled. Simplicity ensures that your instructions are clear and helps to keep your website’s crawling and indexing processes running smoothly.
ii) Don’t Block Essential Pages
Ensure your robots.txt file does not block important pages such as your homepage, blog, or product listings. Blocking vital pages can prevent them from being crawled and indexed, reducing your website’s visibility in search results. Always carefully evaluate your instructions to avoid unintentional limitation of access to important, traffic-generating content.
iii) Use Specific Directives
Using specific directives in your robots.txt file provides exact control over crawler activity. For example, restrict specific files or pages you don’t want to be indexed rather than restricting an entire directory. This method reduces errors and stops redundant content from being hidden. Always test your instructions to ensure they perform as expected.
iv) Update Regularly
Because websites continuously evolve, keeping your robots.txt file updated is important. Regular modifications guarantee that the file reflects the website’s current structure and content strategy. Examine the directives whenever you add, delete, or redesign pages to ensure no sensitive or crucial sections are blocked. Routine maintenance efficiently fixes indexing challenges.
v) Test Your Robots.txt File
Testing your robots.txt file guarantees it functions as planned and prevents important pages from being blocked. Use tools like the Robots.txt Tester in Google Search Console to find errors. Just submit your file, test it, and see what happens. Regular testing keeps your SEO strategy on track and helps ensure good indexing.
vi) Pair with Meta Tags
You can have more control over how search engines interpret your sites by combining robots.txt with meta tags. Meta tags like “noindex” stop certain pages from being indexed, whereas robots.txt prevents bots from crawling. This combination keeps sensitive or low-value content outside search results while giving crucial pages more attention.
By following the above best practices, you can balance privacy and accessibility, ensuring your website ranks well without disclosing sensitive or unnecessary content.
Common Robots.txt Mistakes That Can Block Indexing

When it comes to robots.txt files, even experienced website administrators make errors. These flaws can limit your website’s search engine performance. Let’s discuss a few typical pitfalls:
i) Blocking the Entire Website
Using robots.txt to block your entire website can be a bad idea. A directive like ‘Disallow: /’ prohibits all search engine bots from crawling your website, making it invisible in search results. Always verify your file again to ensure important content is accessible, especially after revisions or redesigns.
ii) Neglecting to Update the File
If you forget to update your robots.txt file, you may end up with outdated rules that permit access to sections meant to remain secret or block important pages. Ensure the file reflects your current structure and objectives as your website develops. Frequent audits keep search engine performance at its best and avoid indexing problems.
iii) Confusion Between Crawling and Indexing
Crawling and indexing are frequently confused. Crawling is when search engine bots check your website for content, whereas indexing involves adding those pages to the search engine’s database. Although it stops crawling, blocking a page in robots.txt does not ensure it will not be indexed. When dealing with confidential content, use “noindex” meta tags.
iv) Overlooking Third-Party Tools
Several external services, CMS platforms, and plugins automatically create robots.txt rules, which could challenge your SEO plan. Ignoring these settings may result in unwanted crawling limits. Regularly check and align these rules with your website’s goals to ensure they don’t block content or interfere with search engine crawling.
v) Not Using Wildcards Wisely
Using wildcards in robots.txt files can be challenging to use. They could block unwanted pages or allow unauthorized access if they are not positioned correctly. For example, blocking all PDF files with `Disallow: /*.pdf` can accidentally restrict important content. Always test wildcard patterns to prevent errors and guarantee accuracy.
Avoiding these errors can help prevent your website from becoming less visible in search results or disclosing personal information.
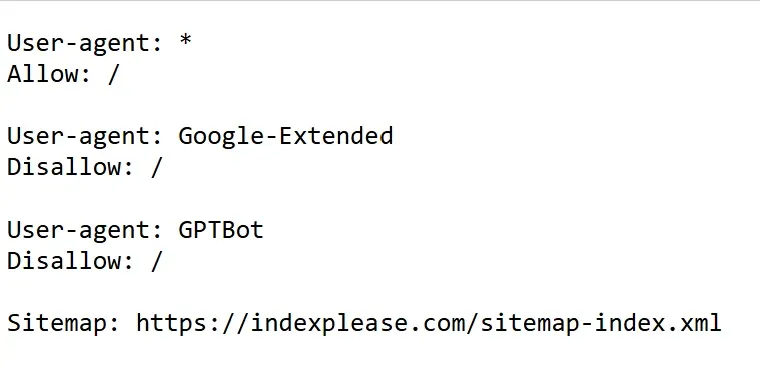
Using Robots.txt with XML Sitemaps for Enhanced Indexing
Combining XML sitemaps with robots.txt is a smart method to enhance indexing and ensure search engines prioritize important pages on your website. XML sitemaps function as a roadmap that directs bots to your most valuable content, while robots.txt acts as a gatekeeper, determining which parts of your website bots can and cannot access. They produce a well-balanced system for effective crawling and indexing.
Including a link to your XML sitemap in your robots.txt file helps search engine bots find and crawl important pages when they visit your site. Search engines do not miss recent changes or deeply placed information. XML sitemaps enhance robots.txt’s control by emphasizing priority pages and adding metadata such as most recent modified dates.
Effective use of both techniques reduces crawl resource waste. For instance, the sitemap ensures that important sections of your website get the required attention, while robots.txt stops bots from accessing private or unnecessary content. This partnership helps search engines provide users with better results while also increasing the visibility of your website.
Maintaining your website’s optimization for search engine crawling and indexing through regular updates to your XML sitemap and checking its link in robots.txt will result in steady organic traffic.
Conclusion
One effective but frequently disregarded item in the SEO toolbox is the robots.txt file. It lets you manage what search engines can and cannot see and allows them to consider only the most important content on your website. You can improve your site’s search engine performance by understanding how robots.txt impacts indexing.
Remember that creating a robots.txt file is just the first step. You can improve your SEO approach by using technologies like XML sitemaps, testing thoroughly, and updating frequently. Understanding robots.txt may help you manage the complexity of search engine optimization and maintain your website’s visibility online, regardless of your experience as a website admin.
FAQs
- What is robots.txt, and why is it important?
Robots.txt is a text file that informs search engine bots what sections of your site they should crawl. It’s vital for optimizing, indexing, and managing bot activity.
- How does robots.txt affect a website’s indexing?
Robots.txt affects indexing by guiding bots to prioritize useful content while avoiding irrelevant or private pages. Misconfigured files might damage visibility by blocking important pages.
- Can robots.txt prevent all pages from being indexed?
No, robots.txt does not completely stop indexing; it only stops bots from crawling certain pages. Use robots.txt directives works with a “noindex” meta tag for sensitive content.
- What are common mistakes to avoid with robots.txt?
Some common mistakes are blocking the entire site, failing to update the file, utilizing wildcards incorrectly, and mixing crawling limitations with indexing controls.
- How do robots.txt and XML sitemaps work together?
XML sitemaps direct bots to important pages, while Robots.txt manages bot access. They increase search engine indexing and crawling efficiency.